
What
are Stem Cells anyway???
Stem
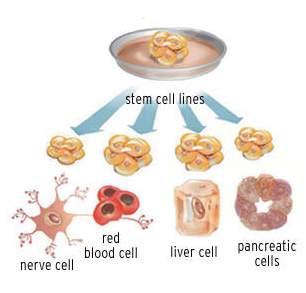
cells are cels that have the ability to divide for indefinite periods in culture
and to give rise to specialized cells.
 The
fertilized egg in a human being is totipotent meaning its potential is total- it
can form an entire organism. In the first few hours after fertilization it
divides into identical totipotent cells. Approximately four days after
fertilization, the blastocyst is formed which as we know has the outer and inner
cell mass. The outer cell mass forms the placenta and the inner cell mass forms
virtually all the tissues in the body.
The
fertilized egg in a human being is totipotent meaning its potential is total- it
can form an entire organism. In the first few hours after fertilization it
divides into identical totipotent cells. Approximately four days after
fertilization, the blastocyst is formed which as we know has the outer and inner
cell mass. The outer cell mass forms the placenta and the inner cell mass forms
virtually all the tissues in the body.
These
inner cell mass cells are pluripotent-they can give rise to many types of cells
but not all types of cells necessary for fetal development. The pluripotent
cells undergo further specialization to committed stem cells which have a
particular function- example- blood stem cells give rise to blood cells of all
types. These more specialized cells are in other words multipotent.
How
are they derived ?
At
present there are two sources of pluripotent stem cells
1)Isolation
directly from the inner cell mass of human embryos at the blastocyst stage.
( The most controversial method) :
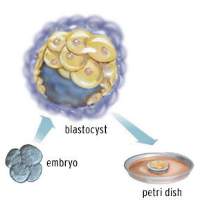 The embryos are from IVF (the ones in excess of the clinical need in infertility
treatment)
The embryos are from IVF (the ones in excess of the clinical need in infertility
treatment)
2)
Isolation from fetal tissue obtained from terminated pregnancies.This
could be done….
3)
The use of somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) may be another
way that pluripotent cells could be isolated. In short, the nucleus of a human
somatic cell is injected into an empty animal ovum. One major advantage is –
we can avoid immune rejection- the nucleus can be from the patient himself.
What
will they be used for ?
1) For the better understanding of certain disease
conditions :
Some of our serious medical conditions like cancer and birth defects are due to
errors in the “decision making” process. A better understanding of the
off-on mechanism will help us to further better research in these areas.
2)
Drug
development:
New medications could be tested on human cell lines, the
advantage in using stem cells being that the drugs can be tested in a wide
variety of cell
3)
“Cell
therapies”:
They may act as a source of renewal and replenishment by
developing into specialized cells.
Examples of Cell therapy include-
- Transplant of healthy heart muscles in patients of chronic heart
disease
- Transplantation of isolated islet cells into the pancreas of
Type 1
Diabetes patients.
- Transplantation of stem cells into the brain of patients with Parkinson’s
disease leading to production of dopamine.
- Persons with severe spinal cord injuries could possibly receive
regenerative cell transplants directly into the spine with little invasive
surgery.
- Cancer chemotherapy patients can benefit from stem cell therapy
which will help them to regenerate healthy blood cells.
Diseases in which stem cell (adult) therapy has
been tried include almost all the leukemias, sickle cell anemia,
myeloproliferative disorders, lymphoproliferative disorders, liposomal storage
diseases, Thalassemia major, Multiple myeloma, neuroblastoma, Ewing sarcoma,
renal cell carcinoma and many others.
![]()