
Current
Research in Stem cells :
Current research into the possible uses of the ES cell is spotty at best. A
biotech firm, Geron Corporation is willing to take financial and moral risk to
support further research. Two Universities at the forefront of such research are
the University of Wisconsin at Madison and John Hopkins University School of
Medicine in Baltimore.
Though not too much has been achieved in this field,
we are just at the opening of a long tunnel and it is not fair to expect to see
light so early. We do have a few nice things to show off.
Indeed, the breakthroughs in stem cell research
reported in the last six months take one’s breath away:
* Italian scientists
have generated muscle tissue using rat stem cells, a discovery that may have
significant implications in organ transplant therapy·
*The group of scientists who cloned Dolly have successfully created heart tissue
using cow stem cells.
*University of South Florida researchers report that rats genetically engineered
to have strokes were injected with rat stem cells that integrated seamlessly
into the surrounding brain tissue appropriate for that part of the brain. This
is amazing- it could mean that stem cell treatments could be used to alleviate
stroke symptoms like slurred speech and dizziness without actual surgery.
But the bottom line is that these results have been achieved with adult stem
cells and not embryonic stem cells.
Oops we seem to have a problem here....
Research has proved that stem cells need specific triggers to develop into the
desired cells and this is no easy task considering that there are about 100
growth factors or triggers that have been identified with new ones being
discovered all the time.
 Other problems faced by scientists is growing cells
in culture whilst preventing them from indiscriminately taking on specialized
roles. When embryonic cells are grown together they have a tendency to try and
re enact development by forming embryoid bodies a mixture of different tissues
like that seen in a teratoma.
Other problems faced by scientists is growing cells
in culture whilst preventing them from indiscriminately taking on specialized
roles. When embryonic cells are grown together they have a tendency to try and
re enact development by forming embryoid bodies a mixture of different tissues
like that seen in a teratoma.
Image
: Electron Microscopic picture of
an embryoid showing clumping of cells without any differentiation. (very early
stage)
 An additional concern is that if undifferentiated embryonic cells were
accidentally injected into a patient along with differentiated cells, they could
develop into a teratoma.
An additional concern is that if undifferentiated embryonic cells were
accidentally injected into a patient along with differentiated cells, they could
develop into a teratoma.
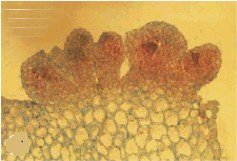
Image
: Simple Microscopic picture of a
embryoid. Note the improper differenciation, with the upper cells appearing like
intenstinal wall cells while the lower cells look like adipose cells.
Some researchers think that embryonic tissue may
provoke the body’s immune response leading to rejection reaction. Even more
alarming, a May 1996 Neurology article disclosed a patient’s death caused by
an experiment in which fetal nerve cells and embryo cells were transplanted into
the brain of a patient with Parkinson’s disease. His death was caused by
undifferentiated cells growing into non neural and therefore deadly tissue.
Are we opening a Pandora’s box?
SO
WHAT ARE WE GOING TO DO NEXT?
Science may have taken a lot of bashing from monarchs
and priests alike, but it has never known to move backwards. There are many
green areas in this field too.
-
This
legislation applies to USA alone. Scientists in UK still continue the
research with new embryonic stem cell lines.
- Some scientists believe that adult bone marrow stem cells could be as
effective as embryonic stem cells in regenerating a specific type of
cell line. An extra step is being taken to try and “de-differentiate” these
cells.- Eventually we hope to get stem cells without using embryos at all by
finding and cloning proteins in ova that lead to creation of stem cells- We also
hope to circumvent the various problems in embryonic stem cell
therapy by perfection of techniques.

Image
: Remember? :) ?
Here
are some of the alternatives to embryonic stem cells and what recent research
shows about their possibilities and limitations:
1)
Placenta
New Jersey
biotech firm, Anthrogenesis Corp., announced Wednesday that it had found a new
kind of stem cell in tissue from the fetal side of theplacenta. Such cells are
neither blood nor adult stem cells, the firm claims.
2)
Cord blood/bone marrow/circulating blood
Cord blood stem cells are much less primitive than embryonic ones, but more
primitive than marrow and circulating blood stem cells, she said.Last month, two
teams of researchers reported they'd used stem cells from bone marrow to repair
heart tissue in rodents. Scientists familiar with the work said it was good but
not convincing evidence that the stem cells had actually produced heart tissue
instead of cells that act and put out signals like heart tissue when prodded
with the right chemicals
3)
Brain cells:
Stem cells have
been obtained from cadavers.
4)
Fat
Researchers say they have isolated adult stem cells from fat removed during
liposuction and converted them into bone, cartilage and muscle.
The
US Congress may have made a decision, but in our minds we have countless
questions and very few answers.
Maybe not for long.
-Roopa
Nishi
(1995 batch )
roopa@kemates.com

![]()